Role Management
When we click Administration / Roles menu, we enter to the role management page:
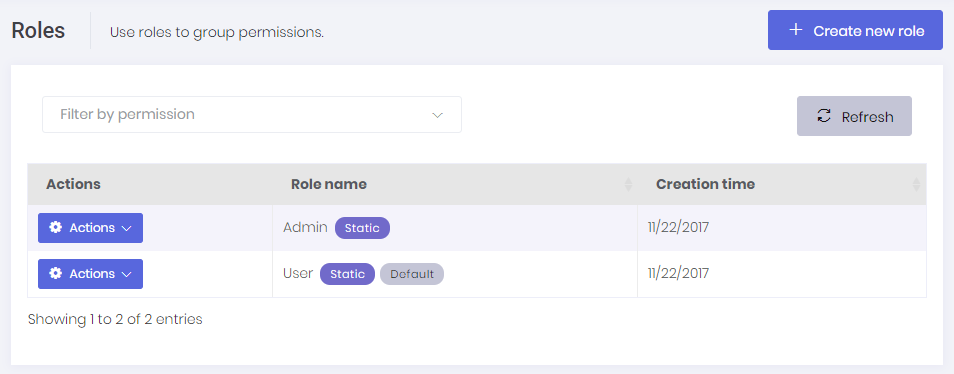
Roles are used to group permissions. When a user has a role, then the user will have all permissions of that role.
A role is represented by the Role class. Role class can be extended by adding new properties.
Roles can be dynamic or static:
- Static role: A static role has a known name (like 'admin') and this name can't be changed. (But the display name can be changed). It's created on the system startup and can not be deleted on the UI. Thus, we can write codes based on a static role name.
- Dynamic role: We can create a dynamic role after deployment. Then we can grant permissions for that role, we can assign the role to some users and we can delete it. We can not know names of dynamic roles in development time.
One or more roles can be set as default. Default roles are assigned to newly added/registered users by default. This is not a development time property and can be set or changed after deployment.
In startup project, we have static admin role for host (for multi-tenant apps). Also, we have static admin and user roles for tenants. Admin roles have all permissions granted by default. User role is the default role for new users and has no permission by default. These can be changed easily in the AppRoleConfig.cs class under "/Authorization/Roles/" folder in the *.Core project.
Static roles are seeded in HostRoleAndUserCreator.cs and TenantRoleAndUserBuilder.cs classes under "Migrations/Seed/" folder in *.EntityFrameworkCore project.
Role Permissions
Since roles are used to group permissions, we can set permissions of a role while creating or editing as shown below:
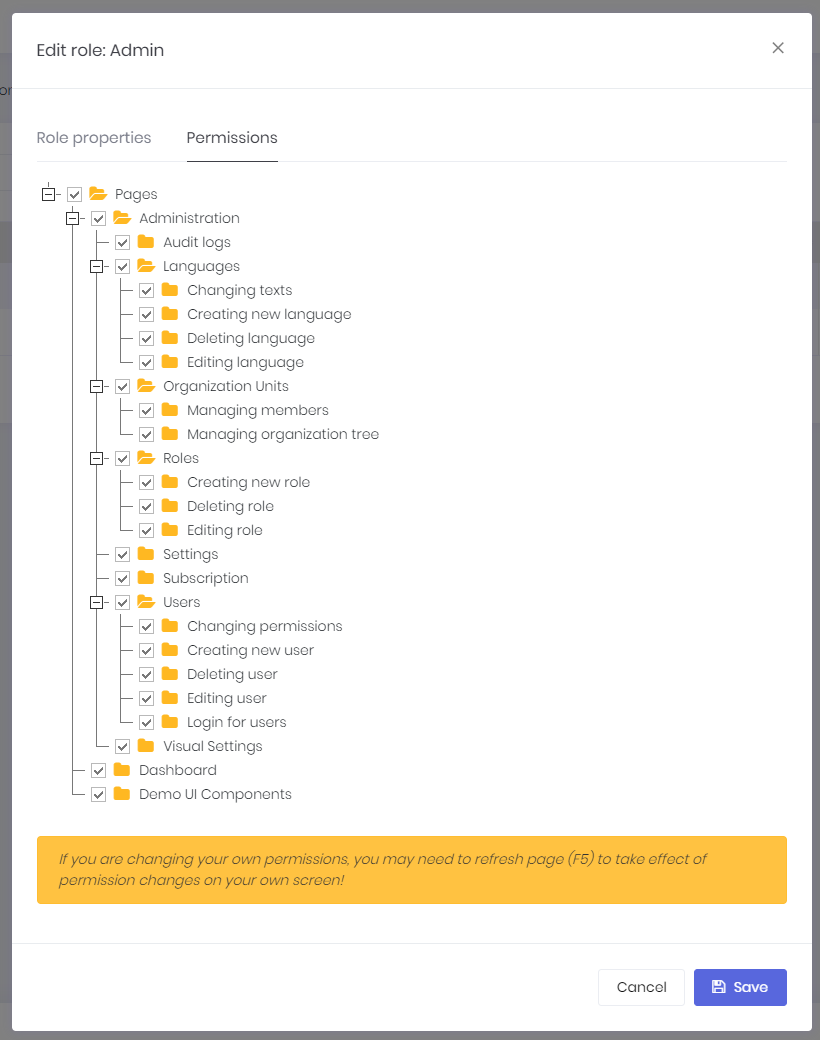
Note that not all permissions shown in the figure above.
Every tenant has it's own roles and any change in roles for a tenant does not effect other tenants. Also, host has also it's own isolated roles.
